 Height and date of the real peak as a function of the detection rate θ
Height and date of the real peak as a function of the detection rate θAbstract
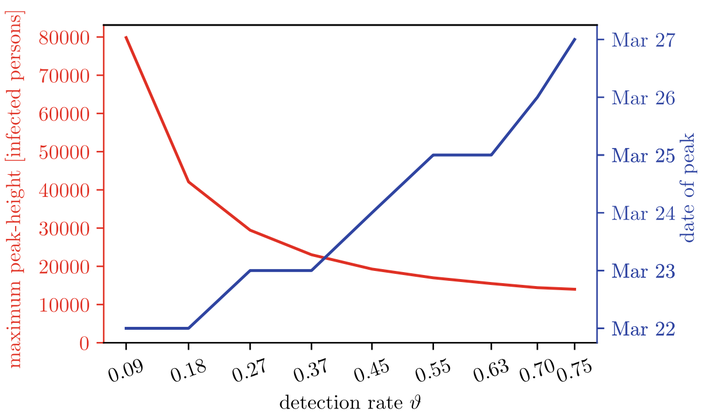
Background Knowing the number of undetected cases of COVID-19 is important for a better understanding of the spread of the disease. This study analyses the temporal dynamic of detected vs. undetected cases to provide guidance for the interpretation of prevalence studies performed with PCR or antibody tests to estimate the detection rate Methods: We used an agent-based model to evaluate assumptions on the detection probability ranging from 0.1 to 0.9. For each general detection probability, we derived age-dependent detection probabilities and calibrated the model to reproduce the epidemic wave of COVID-19 in Austria from March 2020 to June 2020. We categorized infected individuals into presymptomatic, symptomatic unconfirmed, confirmed and never detected to observe the simulated dynamic of the detected and undetected cases. Results: The calculation of the age-dependent detection probability ruled values lower than 0.4 as most likely. Furthermore, the proportion of undetected cases depends strongly on the dynamic of the epidemic wave: during the initial upswing, the undetected cases account for a major part of all infected individuals, whereas their share decreases around the peak of the confirmed cases. Conclusions: The results of prevalence studies performed to determine the detection rate of COVID-19 patients should always be interpreted with regard to the current dynamic of the epidemic wave. Applying the method proposed in our analysis, the prevalence study performed in Austria in April 2020 could indicate a detection rate of 0.13, instead of the prevalent ratio of 0.29 between detected and estimated undetected cases at that time.